Obergefell v. Hodges (2015)
Same-Sex Couples Have a Constitutional Right to Marry
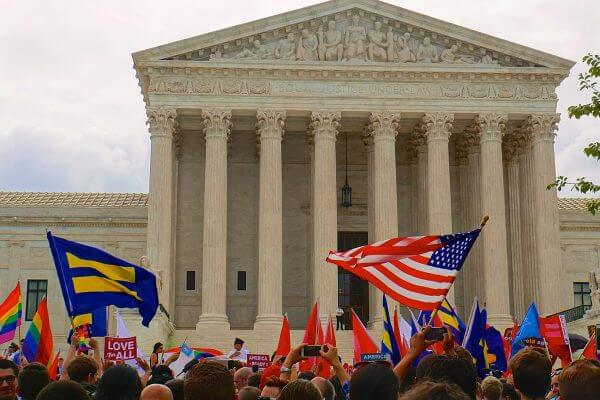
Outside the Supreme Court, the crowd celebrates the Court's decision on the morning of June 26, 2015.
Photo Credit: Ted Eytan, CC BY-SA 2.0
Overview
Federalism divides power between state government and the national government. Marriage is an area that has historically been left to the states resulting in a variety of state marriage laws developed over the 19th and 20th centuries. While the Supreme Court generally did not hear cases arising from disputes regarding marriage law, they did strike down laws that prohibited interracial marriage as unconstitutional in 1967 (Loving v. Virginia). Starting in the 1970s, a handful of states defined marriage as between one man and one woman. In the late 20th century, LGBTQ rights advocates began to challenge these laws and push for marriage equality.
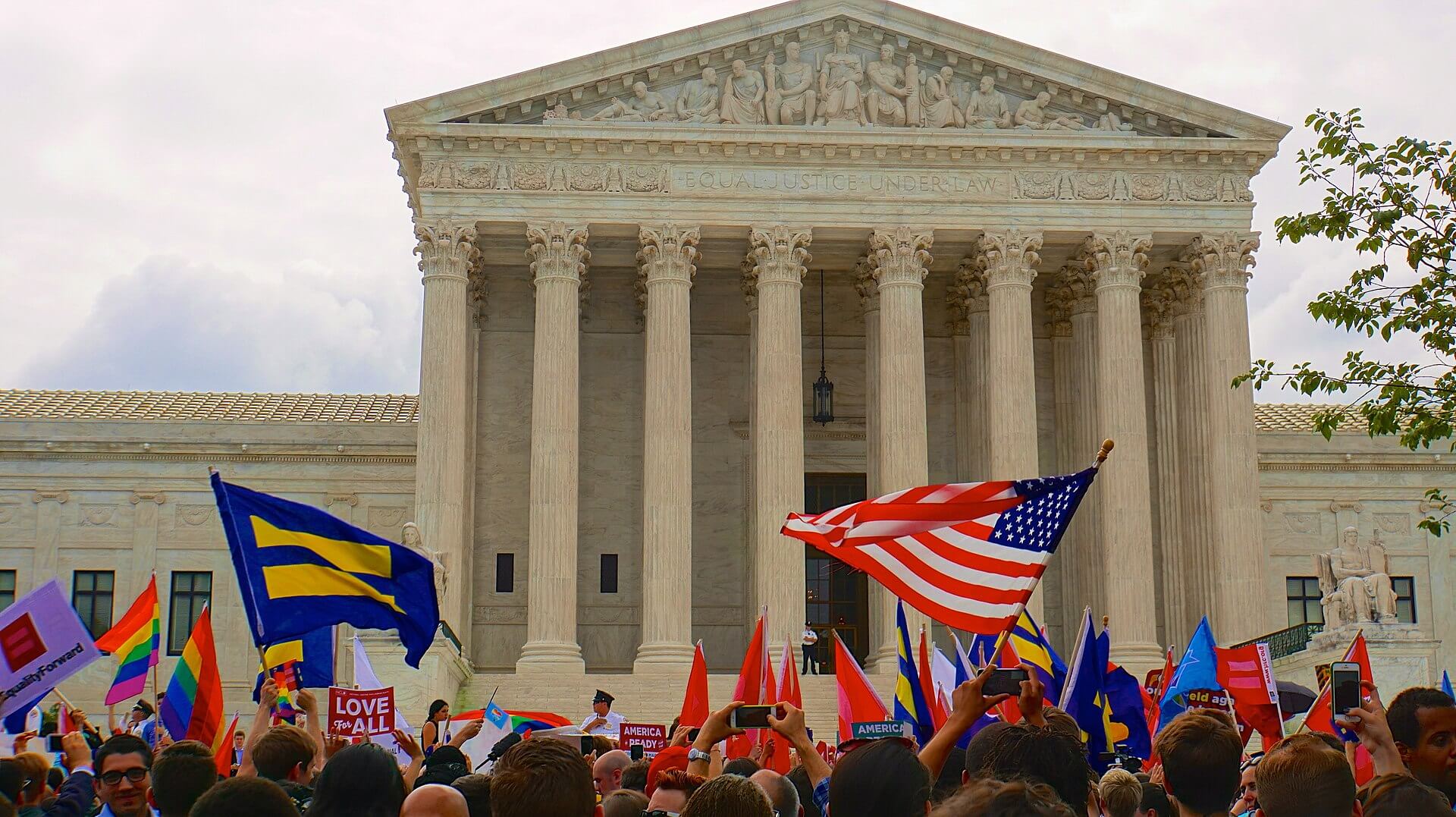

Outside the Supreme Court, the crowd celebrates the Court's decision on the morning of June 26, 2015.
Photo Credit: Ted Eytan, CC BY-SA 2.0
"Marriage is sacred to those who live by their religions and offers unique fulfillment to those who find meaning in the secular realm. Its dynamic allows two people to find a life that could not be found alone, for a marriage becomes greater than just the two persons. Rising from the most basic human needs, marriage is essential to our most profound hopes and aspirations."
- Justice Anthony Kennedy, speaking for the majority
Learning About Obergefell v. Hodges
Students
This section is for students. Use the links below to download classroom-ready .PDFs of case resources and activities.
About the Case
Full Case Summaries
A thorough summary of case facts, issues, relevant constitutional provisions/statutes/precedents, arguments for each side, decision, and case impact.
Case Background and Vocabulary
Important background information and related vocabulary terms.
Learning Activities
Teachers
Use the links below to access:
- student versions of the activities in .PDF and Word formats
- how to differentiate and adapt the materials
- how to scaffold the activities
- how to extend the activities
- technology suggestions
- answers to select activities
(Learn more about Street Law's commitment and approach to a quality curriculum.)
About the Case
- Full Case Summaries: A summary of case facts, issues, relevant constitutional provisions/statutes/precedents, arguments for each side, decision, and impact. Available at high school and middle school levels.
- Case Background: Background information at three reading levels.
- Case Vocabulary: Important related vocabulary terms at two reading levels.
- Diagram of How the Case Moved Through the Court System
- Case Summary Graphic Organizer
- Case Summary Graphic Organizer - Fillable
- Decision: A summary of the decision and key excerpts from the opinion(s)
Learning Activities
After the Case
Teacher Resources
Teaching Strategies Used
Planning Time and Activities
If you have ONE day...
- Read the background summary (•••, ••, •) and answer the questions.
- Complete the Classifying Arguments Activity. Discuss which arguments the students find most convincing.
- For homework, have students read the Key Excerpts from the Opinion and answer the questions. Follow up the next day by reviewing the questions with students.
If you have TWO days...
- Complete the activities for the first day (excluding homework)
- Complete The 14th Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause Activity
- Complete the activities for the first day (excluding the homework).
- For homework, have students read the Key Excerpts from the Opinion and answer the questions. Follow up the next day by reviewing the questions with students.
If you have THREE days...
- Complete the activities for the first and second days (excluding homework)
- Complete the Applying Precedents Activity
- Complete the Unmarked Opinions Activity
If you have FOUR days...
- Complete the activities for the first, second, and third days.
- have students read the Key Excerpts from the Opinion and answer the questions.
- Complete the Political cartoon analysis.
Glossary
These are terms you will encounter during your study of Obergefell v. Hodges. View all Glossary terms here.
Related Cases
Legal Concepts
- These are legal concepts seen in Obergefell v. Hodges. Click a legal concept for an explanation and a list of other cases where it can be seen. View all Legal Concepts here.